| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 프로젝트
- Django
- ART_Cinema
- join()
- 북마크앱
- 장고 프로젝트 순서
- JavaScript
- 파이썬 웹프로그래밍 장고
- Algorithm
- Exercism
- Node.js
- 북마크만들기
- 장고
- 타사인증
- Bookmark
- 개발
- MYSQL
- 장고 개발 순서
- Blog
- Django Blog
- 예술영화추천
- 장고 프로젝트
- MyPick31
- python
- passport.js
- 독립영화플랫폼
- til
- mongodb
- 알고리즘
- 자바스크립트
- Today
- Total
Juni_Dev_log
(LeetCode) Linked List in Binary Tree with Python 본문
🔥 문제
Given a binary tree root and a linked list with head as the first node.
Return True if all the elements in the linked list starting from the head correspond to some downward path connected in the binary tree otherwise return False.
In this context downward path means a path that starts at some node and goes downwards.
Example 1:
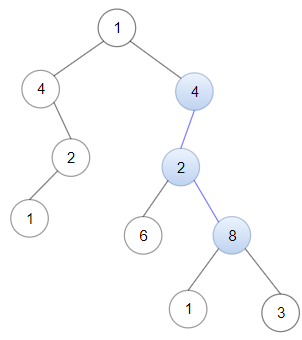
Input: head = [4,2,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3]
Output: true
Explanation: Nodes in blue form a subpath in the binary Tree.
Example 2:

Input: head = [1,4,2,6], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3]
Output: true
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,4,2,6,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3]
Output: false
Explanation: There is no path in the binary tree that contains all the elements of the linked list from head.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range [1, 2500].
- The number of nodes in the list will be in the range [1, 100].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 100 for each node in the linked list and binary tree.
- 연관 배열인 head의 모든 요소들이 해당 root 로 구성된 이진트리에 경로에 해당이 된다면 true / 그렇지 않다면 fasle 를 반환한다.
💯 Solution
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
# head : ListNode / root : ListRoot
def isSubPath(self, head, root):
dataList = []
curListNode = head
# dataList 배열에 curListNode(head)의 값을 넣는다.
while curListNode:
dataList.append(curListNode.val)
curListNode = curListNode.next
#print('dataList = ', dataList)
self.res = False
# self의 data를 추가하고 빈 배열을 추가한다.
self.data = []
# curNode 현재 노드 / curList 현재 리스트
def helper(curNode, curList):
# 현재 노드가 None 이라면
if(curNode == None):
# self.data 배열안에 curList가 없다면
if(curList not in self.data):
# curList를 self.data 배열 안에 추가한다.
self.data.append(curList)
# 현재 노드가 None 이 아니라면 curList 배열과 curNode.val을 합친다.
return
helper(curNode.left, curList+[curNode.val])
helper(curNode.right, curList+[curNode.val])
# root에서 처음 시작하는 재귀함수 실행
helper(root, [])
#print("end self.data = ", self.data)
#self.data 배열을 반복해서 하나씩 꺼내본다.
for data in self.data:
#print('data = ',data)
indexes = []
# data의 배열을 하나씩 꺼내서 본다.
for i in range(len(data)):
num = data[i]
#print('num = ', num)
# dataList의 첫번째 배열값과 data의 배열값이 같아진다면
if (num == dataList[0]):
# indexes 배열에 index를 추가한다.
indexes.append(i)
#print('indexes = ', indexes)
# indexes 배열이 비어있다면 for문을 계속해서 반복한다.
if(indexes == []):
continue
tmpLen = len(dataList)
#print('tmpLen =',tmpLen)
for idx in indexes:
if(data[idx:idx+tmpLen] == dataList):
#print(data[idx:idx+tmpLen])
#print(dataList)
return True
return False
🗂 저장소
github.com/JiHoon-JK/Algorithm/blob/main/LeetCode/test.py
JiHoon-JK/Algorithm
알고리즘 공부를 위한 저장소입니다. Contribute to JiHoon-JK/Algorithm development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'CodingTest > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (LeetCode) House Robber ② with Python (0) | 2021.02.19 |
|---|---|
| (LeetCode) Coin Change with Python (0) | 2021.02.16 |
| (LeetCode) Pizza With 3n Slices with Python (0) | 2021.02.15 |
| (LeetCode) Maximum Width of Binary Tree with Python (0) | 2021.02.09 |
| (LeetCode) Most Frequent Subtree Sum with Python (0) | 2021.02.08 |